Identify the highlighted structure upper limb – Identifying the Highlighted Structures of the Upper Limb:Delving into the intricate anatomy of the upper extremity, this exploration unveils the key structures that orchestrate its remarkable functionality, from the shoulder’s mobility to the hand’s dexterity.
The upper limb, a masterpiece of biomechanics, comprises an array of bones, joints, and muscles that work in harmonious concert to facilitate a vast repertoire of movements. This discourse embarks on a journey to pinpoint the prominent anatomical landmarks that define this region, unraveling their location, shape, and the pivotal roles they play in our everyday interactions.
Overview of the Upper Limb
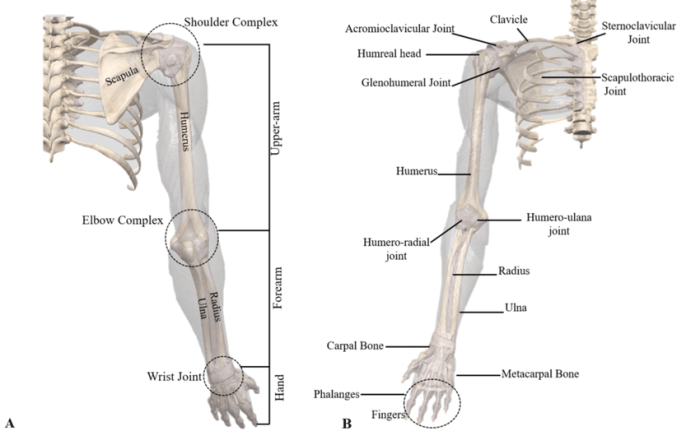
The upper limb, consisting of the shoulder, arm, forearm, wrist, and hand, is a highly versatile and intricate structure that enables a wide range of movements and functions. It comprises numerous bones, joints, muscles, blood vessels, and nerves that work in harmony to facilitate activities such as reaching, grasping, lifting, and fine motor control.The
upper limb’s functional significance is evident in its role in daily tasks, from basic self-care activities to complex skilled movements. It plays a crucial part in communication through gestures and sign language, as well as in creative pursuits such as painting, writing, and playing musical instruments.
Identification of Key Structures
The upper limb is characterized by several prominent anatomical landmarks that serve as reference points for surgical and diagnostic procedures. The shoulder joint, formed by the articulation of the humerus with the scapula, allows for a wide range of movements, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation.Moving
down the limb, the elbow joint, where the humerus meets the radius and ulna, facilitates flexion and extension of the forearm. The wrist joint, formed by the distal ends of the radius and ulna articulating with the carpal bones, allows for flexion, extension, radial and ulnar deviation, and circumduction.The
hand, a highly specialized structure, consists of the carpus, metacarpus, and phalanges. The carpus, comprising eight small bones, provides stability and flexibility to the wrist. The metacarpus, consisting of five long bones, forms the palm of the hand. The phalanges, fourteen in total, make up the fingers and thumb, enabling precise and intricate movements.
Musculature of the Upper Limb, Identify the highlighted structure upper limb
The upper limb’s musculature is divided into various groups based on their location and function. The shoulder muscles, including the deltoid, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor, are responsible for shoulder movements such as flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation.The arm muscles, primarily the biceps brachii and triceps brachii, facilitate flexion and extension of the elbow joint.
The forearm muscles, including the flexor and extensor groups, control wrist and finger movements. The intrinsic hand muscles, located within the hand itself, enable fine motor control and dexterity.
Blood Supply and Innervation
The upper limb is supplied by several major arteries, including the axillary artery, brachial artery, and radial and ulnar arteries. These arteries branch out into a network of smaller vessels that provide oxygenated blood to the muscles, bones, and other tissues.Innervation
of the upper limb is primarily provided by the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that originates from the cervical spinal cord. The brachial plexus gives rise to various nerves, including the median nerve, ulnar nerve, and radial nerve, which supply sensory and motor function to different regions of the upper limb.
Imaging Techniques
Various imaging techniques are employed to visualize the upper limb and assess its structures. X-rays provide a two-dimensional view of the bones, revealing fractures, dislocations, and other bony abnormalities. Computed tomography (CT) scans utilize X-rays to generate cross-sectional images, offering more detailed information about bones, muscles, and other soft tissues.Magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI) utilizes magnetic fields and radio waves to produce high-resolution images of the upper limb, particularly soft tissues such as muscles, tendons, and ligaments. These imaging techniques play a crucial role in diagnosing and assessing a wide range of upper limb conditions, guiding treatment plans and monitoring outcomes.
FAQ: Identify The Highlighted Structure Upper Limb
What is the significance of the shoulder joint in upper limb function?
The shoulder joint, a ball-and-socket articulation, provides a wide range of motion, enabling the arm to reach, rotate, and abduct.
How do the muscles of the upper limb contribute to its functionality?
The muscles of the upper limb, categorized into flexors, extensors, abductors, and adductors, work in synergy to control movement, maintain posture, and provide stability.