As Unit 7 SAQ AP World History takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with depth and clarity, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Delving into the heart of this historical epoch, Unit 7 SAQ AP World History unveils the rise and fall of civilizations and empires, the transformative cultural and intellectual developments that shaped societies, and the intricate web of global connections and exchanges that left an indelible mark on the course of human history.
Historical Context
Unit 7 of the AP World History curriculum delves into the era of the Global Age, spanning from 1750 to the present. This pivotal period witnessed profound transformations in global interconnectedness, technological advancements, and political and economic landscapes.
The unit explores the major themes that shaped this era, including the rise of industrialization, imperialism, nationalism, and globalization. It examines the interconnectedness of different regions of the world and the ways in which events in one part of the globe had far-reaching consequences for others.
Major Events and Themes
- Industrial Revolution: The technological and economic changes that transformed production, transportation, and communication.
- Imperialism: The expansion of European powers into Africa, Asia, and the Americas, leading to political and economic domination.
- Nationalism: The rise of national identities and movements, often leading to the creation of new nation-states.
- Globalization: The increasing interconnectedness of the world through trade, communication, and cultural exchange.
- World Wars: The two global conflicts that had a profound impact on political, economic, and social structures.
- Decolonization: The process of independence movements in former colonies, leading to the creation of new nation-states.
- Cold War: The ideological conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union, which shaped global politics for decades.
Major Civilizations and Empires
Unit 7 explores the rise and fall of major civilizations and empires, shaping the course of world history. These civilizations left indelible marks on culture, technology, and governance, influencing the development of subsequent societies.
Mesopotamia
- Emerged in the Fertile Crescent, developing cuneiform writing, mathematics, and astronomy.
- Flourished through city-states like Ur and Babylon, with a centralized government and advanced irrigation systems.
Ancient Egypt
- Arose along the Nile River, known for its monumental architecture, including pyramids and temples.
- Developed hieroglyphics, a written language, and advanced mathematical concepts.
Ancient Greece
- Flourished in the Mediterranean region, renowned for its philosophy, literature, and democratic government.
- Contributions include the development of Western philosophy, the Olympic Games, and advancements in mathematics and science.
Ancient Rome
- Expanded from the Italian Peninsula, establishing a vast empire that influenced European and Mediterranean civilizations.
- Known for its legal system, infrastructure, and architectural achievements, including the Colosseum and the Pantheon.
Han Dynasty China, Unit 7 saq ap world history
- Established a centralized empire in East Asia, ushering in a golden age of Chinese civilization.
- Contributions include the development of papermaking, the compass, and the Silk Road trade network.
Gupta Empire India
- Flourished in the Indian subcontinent, fostering advancements in mathematics, astronomy, and literature.
- Known for its religious tolerance, the development of the Gupta script, and the creation of the zero concept.
Interactions and Conflicts
These civilizations and empires interacted and clashed, shaping the course of history. Trade routes facilitated the exchange of ideas, goods, and technologies. However, conflicts over territory, resources, and ideologies also occurred.
- The Greco-Persian Wars exemplified the clash between Eastern and Western civilizations.
- The Roman Empire’s expansion brought it into conflict with various civilizations, including the Gauls and the Parthians.
- The Silk Road connected East and West, fostering cultural and economic exchange, but also leading to conflicts between empires.
Cultural and Intellectual Developments

Unit 7 witnessed a surge of cultural and intellectual advancements that profoundly shaped the societies of the time. From the spread of religions to the emergence of new technologies and artistic styles, these developments left an enduring legacy on human civilization.
Spread of Religions
During this period, several major religions gained prominence, including Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam. These religions offered new spiritual beliefs and ethical frameworks, influencing social structures, values, and daily life. The spread of religions also facilitated cultural exchange and the transmission of ideas across vast distances.
Technological Advancements
Technological innovations played a pivotal role in shaping societies during Unit 7. The development of ironworking and the invention of the plow revolutionized agriculture, leading to increased food production and population growth. Maritime technologies, such as the compass and astrolabe, enabled exploration and trade, connecting different regions of the world.
Artistic Developments
The artistic landscape of Unit 7 was characterized by a rich tapestry of styles and influences. From the naturalistic sculptures of ancient Greece to the vibrant murals of the Maya civilization, art reflected the cultural and spiritual values of the time.
New artistic techniques, such as perspective and foreshortening, emerged, expanding the possibilities of artistic expression.
Impact on Societies
The cultural and intellectual developments of Unit 7 had a profound impact on societies. The spread of religions fostered a sense of community and provided a moral compass for individuals. Technological advancements improved living standards and facilitated economic growth. Artistic developments enriched cultural life and stimulated creativity and innovation.
Global Connections and Exchanges: Unit 7 Saq Ap World History

During Unit 7, the world witnessed a surge in global connections and exchanges that profoundly shaped its development. These interactions encompassed trade, migration, and the spread of ideas, leaving an indelible mark on civilizations and cultures across vast distances.
Trade
Trade flourished along established routes such as the Silk Road, connecting East and West. Merchants exchanged goods like silk, spices, and precious stones, facilitating the diffusion of technologies, artistic styles, and religious beliefs. This vibrant trade fostered economic growth and cultural exchange, creating cosmopolitan centers and enriching societies with diverse influences.
Migration
Large-scale migrations occurred throughout the period, driven by factors such as war, famine, and religious persecution. The movement of peoples, including the Bantu expansion in Africa and the Mongol conquests in Asia, introduced new ideas, technologies, and genetic diversity to recipient regions.
These migrations often led to cultural blending and the emergence of new civilizations.
Spread of Ideas
Ideas traveled far and wide during Unit 7. Religions like Buddhism and Christianity spread from their origins in Asia to distant lands, transforming spiritual beliefs and social structures. Philosophical and scientific concepts from Greece and India found their way to other regions, influencing intellectual thought and the development of new knowledge systems.
The exchange of ideas fostered cultural synthesis and stimulated intellectual growth.
Unit 7 of the SAQ AP World History course delves into the complex factors that led to the American Civil War. To gain a deeper understanding of this pivotal conflict, I highly recommend exploring the comprehensive analysis provided in the article “Causes of the Civil War DBQ” ( causes of the civil war dbq ). By examining primary and secondary sources, this resource offers a nuanced perspective on the underlying tensions that ultimately erupted into war.
As you continue your exploration of Unit 7, this article will serve as a valuable complement to your studies.
Primary Source Analysis
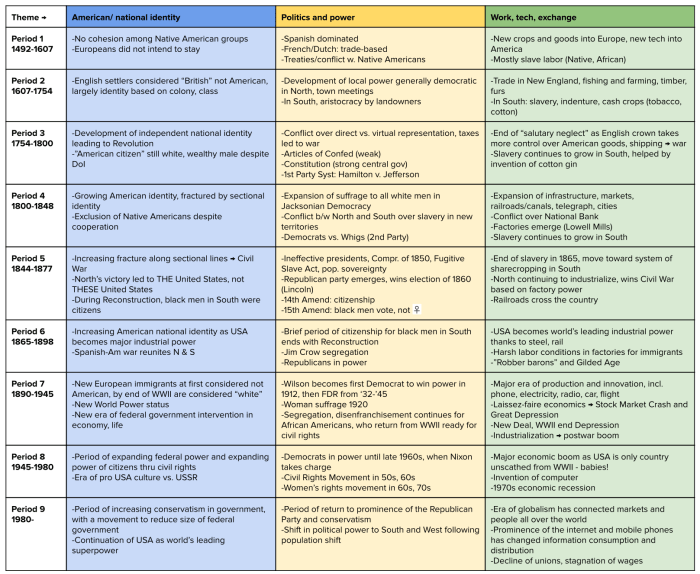
Primary sources are firsthand accounts of past events, created during the time period being studied. They can provide valuable insights into the past, but they also have limitations that researchers must be aware of.
Examples of primary sources from Unit 7 include:
- The Code of Hammurabi, a Babylonian law code from the 18th century BCE
- The Epic of Gilgamesh, a Mesopotamian epic poem from the 21st century BCE
- The Analects of Confucius, a collection of sayings and teachings from the Chinese philosopher Confucius from the 5th century BCE
- The Arthashastra, an Indian political treatise from the 4th century BCE
- The Rosetta Stone, a stone inscribed with a decree in three scripts from the 2nd century BCE
These sources can be used to understand the past in a variety of ways. For example, the Code of Hammurabi provides insights into the legal system of ancient Babylonia, while the Epic of Gilgamesh offers a glimpse into the religious beliefs and social values of the ancient Mesopotamians.
Strengths and Limitations of Primary Sources
Primary sources have a number of strengths. They are:
- Firsthand accounts:Primary sources are firsthand accounts of past events, which means that they provide a unique perspective on the past.
- Detailed:Primary sources can be very detailed, providing a wealth of information about the past.
- Authentic:Primary sources are authentic documents, which means that they have not been altered or changed.
However, primary sources also have a number of limitations. They are:
- Biased:Primary sources can be biased, as they are written from the perspective of the author.
- Incomplete:Primary sources can be incomplete, as they may not contain all of the information about a particular event.
- Difficult to interpret:Primary sources can be difficult to interpret, as they may be written in a language or style that is unfamiliar to the reader.
Despite their limitations, primary sources are essential for understanding the past. By carefully considering the strengths and limitations of primary sources, researchers can use them to gain a more accurate and complete understanding of the past.
Historical Interpretation and Historiography

In studying history, it is essential to recognize that historical events and themes are often subject to varying interpretations. These interpretations are shaped by a variety of factors, including the historian’s perspective, the available sources, and the prevailing historiographical trends.
Historians play a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the past. They analyze historical sources, evaluate evidence, and construct narratives that help us make sense of past events. Their interpretations are influenced by their own biases, values, and the theoretical frameworks they employ.
Historiographical Trends
Historiography refers to the study of historical writing and the methods used by historians to interpret the past. Over time, different historiographical trends have emerged, each with its own unique approach to historical analysis.
- Traditional historiographyfocused on political and military events, with an emphasis on the role of great leaders.
- Social historyemerged in the 19th century, emphasizing the experiences of ordinary people and the social structures that shaped their lives.
- Marxist historiography, developed by Karl Marx, viewed history as a struggle between classes, with economic factors playing a dominant role.
- Postmodern historiography, which gained prominence in the late 20th century, questioned the objectivity of historical knowledge and emphasized the role of narrative and interpretation.
Historical Interpretation and Unit 7 Themes
The events and themes covered in Unit 7 have been interpreted in various ways by historians. For example, the rise of Islam has been attributed to a combination of religious, economic, and political factors, and its impact on the world has been debated by scholars.
Similarly, the Mongol conquests have been interpreted as both a destructive force that disrupted trade and cultural exchange, and as a transformative force that facilitated the spread of ideas and technologies.
Conclusion
Historical interpretation is an ongoing process that is constantly evolving as new sources are discovered and new perspectives are developed. By understanding the different interpretations of the past, we can gain a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding of human history.
Historical Thinking Skills
Unit 7 provides ample opportunities to develop students’ historical thinking skills. These skills are essential for understanding and analyzing historical events and processes, and they can be applied to a wide range of academic and professional pursuits.
Historical thinking skills include critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and the ability to interpret evidence and construct historical narratives.
Critical Thinking
Unit 7 can be used to develop students’ critical thinking skills by encouraging them to question historical sources, identify biases, and evaluate the reliability of evidence. Students can also be asked to analyze different perspectives on historical events and to form their own interpretations.
- For example, students can be asked to compare and contrast different accounts of the American Revolution or to analyze the role of propaganda in World War II.
Problem-Solving
Unit 7 can be used to develop students’ problem-solving skills by encouraging them to identify and solve historical problems. Students can be asked to develop solutions to real-world problems that are based on historical knowledge, or they can be asked to create historical simulations that allow them to experience the challenges of making historical decisions.
- For example, students can be asked to develop a plan to solve the problem of poverty in the United States or to create a simulation of the Cuban Missile Crisis.
Communication
Unit 7 can be used to develop students’ communication skills by encouraging them to write, speak, and present about historical topics. Students can be asked to write essays, give presentations, or create multimedia projects that demonstrate their understanding of historical events and processes.
- For example, students can be asked to write an essay about the causes of the Civil War or to give a presentation about the impact of the Industrial Revolution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of Unit 7 SAQ in the AP World History curriculum?
Unit 7 SAQ plays a crucial role in the AP World History curriculum by providing a comprehensive examination of the major civilizations, empires, and global connections that shaped the world from 1450 to 1750.
What are the key themes covered in Unit 7 SAQ?
Unit 7 SAQ explores a range of themes, including the rise and fall of civilizations and empires, the spread of religions, the development of new technologies, the emergence of new artistic styles, and the impact of global connections and exchanges.
How can Unit 7 SAQ help students develop historical thinking skills?
Unit 7 SAQ provides opportunities for students to develop critical thinking skills, such as analyzing primary sources, evaluating historical interpretations, and constructing well-reasoned arguments based on historical evidence.